Key Takeaways
-
Machine Learning works with structured data and needs human guidance.
-
Deep Learning uses neural networks to handle complex, unstructured data automatically.
-
ML is faster and simpler, while DL needs more data and computing power.
-
Both are essential for AI applications, but the choice depends on task complexity and data type.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the way we live, work, and interact with technology. AI is omnipresent, from our phones’ virtual assistants to Netflix’s recommendation systems, quietly making judgments and boosting efficiency. For newcomers, AI can appear difficult, but understanding the fundamentals helps to demystify this intriguing field. This guide covers the fundamental principles, terminology, applications, and abilities required to begin investigating AI.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
AI is fundamentally concerned with building machines capable of doing activities that require human-like intellect. These tasks include learning from experience, problem solving, language interpretation, pattern recognition, and decision making. Unlike traditional computer programs, which adhere to specific instructions, AI systems can adapt and develop as they process data.
For example, when you use a navigation app, AI calculates the shortest route based on real-time traffic data, learning from patterns in your regular commute. AI is not a single technology; it is a combination of computer science, data analysis, and algorithms that enable machines to behave intelligently.
Essential AI Terms You Should Know
It’s helpful to grasp a few basic terms before delving into AI applications and kinds.

Machine Learning (ML)
A kind of artificial intelligence called machine learning (ML) enables computers to learn from data instead of explicit commands. ML functions similarly by identifying patterns in data, much like teaching a child to recognize animals through photographs. Email spam filters are a typical example; they are not manually programmed for every situation; instead, they learn over time which messages are unwelcome.
Deep Learning (DL)
A more sophisticated type of machine learning called deep learning (DL) analyzes complicated datasets using artificial neural networks. Deep learning works especially well with unstructured data, such as language, photos, and videos. For example, deep learning enables social media apps’ facial recognition systems to reliably recognize faces in a variety of lighting conditions and viewpoints.
Neural Networks
Computational structures called neural networks are modeled after the human brain. They are made up of layers of linked “neurons” that analyze data to find patterns and insights. Deep learning is based on neural networks, which enable computers to solve tasks like voice commands and handwriting recognition that call for pattern recognition.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Machines can comprehend and produce human language thanks to Natural Language Processing (NLP). Chatbots, virtual assistants, and translation services are powered by it. For instance, NLP is used by Google Translate to translate texts between languages, while chatbots driven by AI assist companies in providing prompt customer service.
Computer Vision
AI systems can comprehend visual data from the environment thanks to computer vision. Computer vision enables robots to “see” and react to visual input, from autonomous cars identifying people to medical AI identifying malignancies in scans.
Lastly, Reinforcement Learning is a method by which AI improves decisions based on feedback through trial and error. Though more sophisticated, it helps machines maximize their activities over time and is utilized in autonomous systems, robotics, and game-playing AI.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
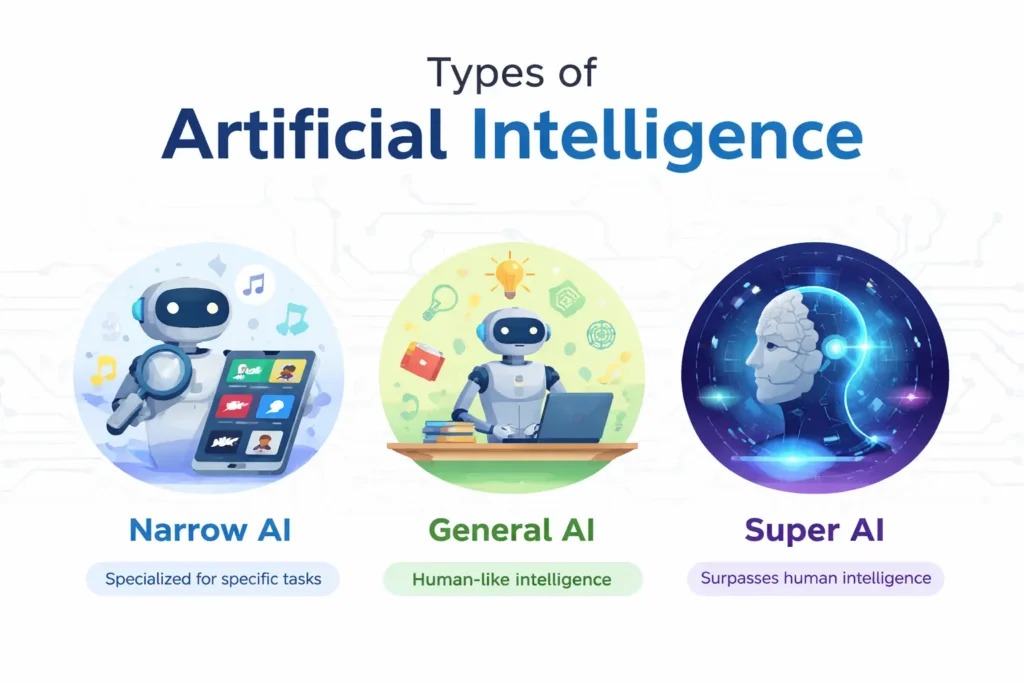
Based on capacity, AI is typically divided into three categories.
Narrow AI
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is made to carry out a single task. It powers image recognition software, virtual assistants, and recommendation systems, making it the most prevalent type of AI available today. Narrow AI is efficient at its intended goal, but it is unable to adapt to tasks that fall outside of its purview.
General AI
General AI, also called Strong AI, is a hypothetical concept where machines can perform any intellectual task a human can. General AI would require reasoning, problem-solving, and learning across different domains. While it remains a goal for researchers, no system currently achieves this level of intelligence.
Super AI
Super AI goes even further, it refers to machines surpassing human intelligence across every field. Super AI is largely theoretical, raising ethical and safety considerations for the future. Most AI we encounter today remains narrow AI, excelling at specific, well-defined tasks.
Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning
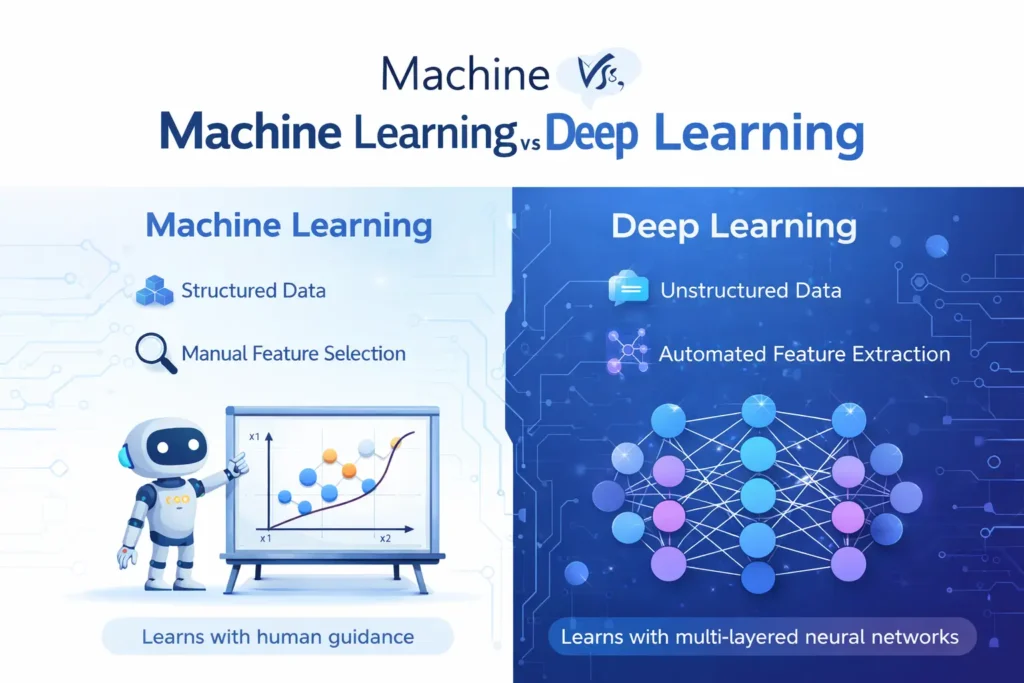
Machine learning and deep learning are often mentioned together, but they are not the same. Machine learning relies on structured data and often requires manual feature selection, meaning humans decide which parts of the data are important for the model. Deep learning, in contrast, handles complex, unstructured data automatically, extracting patterns from images, videos, or text with minimal human input.
For example, a machine learning system might predict house prices based on historical data such as square footage or location, while a deep learning system can identify objects in photos or understand spoken commands in real time. Deep learning is more resource-intensive but highly effective for complex tasks.
Read More: Real-World Applications of AI
How Neural Networks Work
Neural networks are built with layers: an input layer receives data, hidden layers process it using mathematical functions, and an output layer produces predictions. These layers work together to analyze data and identify patterns. Through a process called training, the network adjusts its internal parameters to reduce errors and improve accuracy.
A practical example is handwritten digit recognition. Each layer of the network examines features such as lines, curves, and shapes, gradually building an understanding that allows the system to correctly identify the number, even when written differently each time.
Common AI Algorithms
AI systems rely on algorithms to process data. Supervised learning uses labeled datasets, teaching machines to map inputs to known outputs, such as predicting a student’s exam score based on past performance. Unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data, like grouping customers based on shopping habits. Reinforcement learning, as mentioned earlier, helps AI optimize decision-making through feedback and rewards.
Understanding these algorithms gives insight into how AI “thinks” and adapts to different scenarios.
AI in Everyday Life
AI is more present in daily life than many people realize. Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant help manage tasks, answer questions, and control smart devices. Recommendation systems on streaming platforms like Netflix or Spotify suggest content tailored to your preferences. In healthcare, AI supports diagnostic tools that detect diseases from scans, while in finance, it helps prevent fraud and assists with trading strategies. Even transportation benefits from AI, with smart traffic management and the development of self-driving cars.
AI’s presence in everyday life demonstrates its ability to improve efficiency, convenience, and personalization.
AI and Robotics
AI is often paired with robotics to create machines that can perform physical tasks intelligently. Autonomous drones, industrial robots, and surgical robots combine AI’s decision-making with robotic hardware to execute tasks autonomously or assist humans. For example, surgical robots guided by AI can perform delicate procedures with precision beyond human capabilities, while autonomous drones use AI to navigate complex environments safely.
Ethical Considerations in AI
As AI advances, ethical considerations become increasingly important. AI systems can inherit biases from their training data, unintentionally favoring certain groups over others. Transparency in AI decision-making is crucial, especially when outcomes affect people’s lives, such as in healthcare or criminal justice. Accountability is another concern when AI makes a mistake; it’s not always clear who is responsible. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and safety is vital to the responsible development and use of AI.
Key Skills to Get Started with AI
Learning AI requires a combination of mathematics, programming, and practical experience for novices. Python and R are popular programming languages, and you can create and train models effectively with libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch. Since AI algorithms are based on these ideas, it’s also critical to comprehend probability, linear algebra, and fundamental statistics.
Experience in the real world is crucial. Converting theory into practical abilities is facilitated by working on little tasks like creating a chatbot or analyzing datasets. While online seminars and courses help you stay up to date with the latest developments in AI, platforms like Kaggle and GitHub offer resources for practice and teamwork.
Bottom Line
Artificial intelligence is a significant aspect of the modern world and is no longer a future idea. You can confidently explore this field by gaining an awareness of the fundamentals, important concepts, and applications of artificial intelligence. Artificial Intelligence (AI) permeates almost every facet of contemporary life, from machine learning to deep learning, NLP, computer vision, and robotics. Learning AI is about more than simply technology; it’s about getting ready for a time when intelligent systems will be crucial in forming civilization.
References:

